
As you plan the launch of a new product, you need to understand your customers’ current views of the competitive landscape. This understanding impacts your marketing strategy and how you can best position your new product. The most common way to do this is through a perceptual map.
A perceptual map visualizes what customers think of each competing product's position. These consumer perceptions help you understand how you can earn the market’s interest. When you know what customer needs are not being fully met, you can create a product position and gain the attention of the target market.
Find out what a perceptual map is, how you can create this visual tool, and most importantly, what to do with the results.
What is perceptual mapping exactly?
A perceptual map is a visual tool used by business owners as well as managers to represent market opportunities. Perceptual maps, like other positioning maps, illustrate attributes in a visualization.
But, different from a product positioning map, perceptual mapping is based on what customers perceive, even if that differs from what companies intended to portray. This is to say that perceptual maps reflect consumer views rather than actual traits of the product.
For example, a mobile phone company's product may have a longer battery life than competing brands, but consumers may have a different perception. Learning these perceptions can direct companies to make changes in their marketing strategies.
What are the types of perceptual maps?
The most common style of perceptual map is a two-dimensional perceptual map. It represents two different and competing attributes that are important to the consumer, such as convenience and affordability. When you create perceptual maps, you will add data reflecting each competitor's actual position and clarify the customer perception of different brands relative to each other as well as individually. Perceptual mapping makes it easier to interpret survey data.
Other types of perceptual maps include:
- Multi-dimensional maps
- Attribute-based perceptual maps
- Price-quality perceptual maps
- Preference maps
- Brand-positioning maps
What can perceptual mapping offer a new business?
Investing in a perceptual map can ensure a new business succeeds. Whether that means giving your sales teams perceptual maps for a marketing focus or how you select your product or service in the first place. Some of the benefits of perceptual mapping are...
Promoting the strengths of your brand
Perceptual mapping shows accurate customer views of your brand and your competitors. This knowledge helps identify strengths and weaknesses that you can focus on in your marketing campaigns.
By promoting your strengths to those who value the attribute, you can attract more customers and build brand loyalty in the segment.
Locating market gaps
Gaps in the market are easy to see through perceptual maps and can become a strategic opportunity with little competition.
However, bear in mind that seeing market gaps does not necessarily confirm if the market is a viable prospect. For example, companies may not be active in that market segment because the segment is not profitable due to its size or difficulty to reach.
Understanding your competitors
If you are opening a new business, you will want to understand as much as you can about your competition.
When you visualize the competitive landscape in a perceptual map, you will see your direct competitors. This information supports further development to craft a competitive advantage in your customer’s mind.
Making strategic decisions
Strategic decision making can stem from perceptual maps. By uncovering important information about the market and competition, you can use the data to build a long-term plan and overall business strategy.
Making better use of marketing resources
Perceptual mapping can make your marketing budget more effective. It allows you to hone clear messaging to the target market. By allocating marketing resources that tailor your message and research interested customers, you can build strong brand loyalty in the market.
4 Steps to create a two-dimensional perceptual map
To create an accurate perceptual map, follow these four steps.
1. Identify your goal and how you will use the information.
For a new entrant into the market, the goal may be to better understand market opportunities or to identify a market strategy for a new product. By knowing your goal up front, you will better select the product attributes and ultimately interpret and use the map’s result to achieve your objective.
2. Establish the brand attributes you want to measure.
Using a two-dimensional map, two attributes will be plotted. These are aspects of the brand that are important to the consumer, not to the companies selling the products. While price and quality are commonly used, often consumers have other considerations in mind when making a purchasing decision.
For example, in the cold cereal industry, you might select nutritional value and tastiness. In the luxury automobile industry, you might select comfort and status. The two attributes selected should be the key ones to your customer. What influences them when they make a purchase?
3. Conduct market research and collect customer opinion.
Seek out what customers think of your competitors in relation to the attributes you want to target. This data can be found using surveys, focus groups, feedback interviews, and third-party market data. After collecting the customer data, you will score the results that accurately represent the findings.
4. Plot the results of your data.
Create an X and Y axis representing the spectrum of the two attributes you've chosen, and enter the scores to identify where each brand belongs based on what customers perceive. The selected attributes act as anchors for your perceptual map. With each brand position noted, you have a visual representation of the market in the eyes of your customers.
For example, here's an example of a perceptual map I created for a video game system where important attributes involved social involvement and system complexity. You can see a market gap for a video game system that is simple in design and antisocial. It is possible that there is not sufficient market demand for that category.
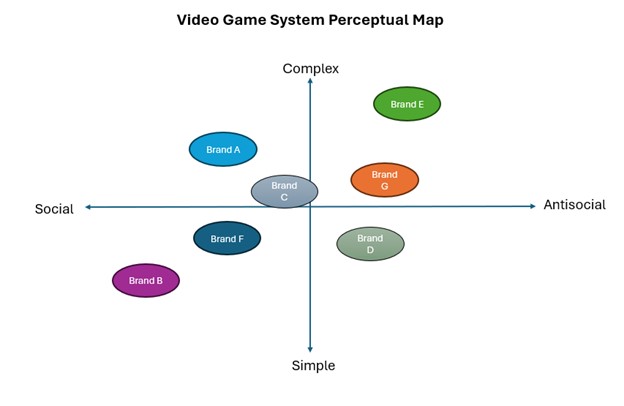
Using perceptual maps to build your product position
This is the most important aspect of perceptual mapping--how do you make good use of your insights?
Remember the first step of the mapping process was to identify your goal. Use that goal to guide you in using the results. If your goal as a new business was to identify a market for a new product, you may want to look closely at potential market gaps.
Let’s assume in the case of the video game system map above, your goal was to create the marketing strategy for your new product launch. Knowing that you have developed a new video game system designed to be both highly complex and social, you see that your primary competitor in that area is Brand A. So, you know you should study Brand A’s marketing and sales strategy closely to see how to build a competitive edge over them.
Additionally, you notice that Brand B has succeeded in its products being perceived as social and Brand E is seen as complex in your customers’ minds. So, in developing sales strategies, you would review those two brands as well to understand how they have captured the market’s perception.
You can see how these specific aspects of study make better use of resources than a full competitive analysis for all competing brands in this market.
Using perceptual maps for ongoing improvements
While we've focused here on the value of understanding customer perceptions for new businesses, perceptual maps are useful throughout the product or brand life cycle. Through continual market research, you can use perceptual mapping to illustrate the customers view of your brand identity.
Marketing teams can use ongoing perceptual mapping to gauge the impact of new competitor products as well. The marketing team will monitor the intended product position and create sales strategies to drive customer engagement and satisfaction.
Perception is a key business driver. By seeing the competitive landscape in the customer's mind, you can identify available market segments and build your marketing strategy to position your product in a desirable way to the target audience.
Whatever a business might intend for their brand identity, ultimately, it is the consumer who determines the result.
Strategy can make all the difference
As you can see, businesses that take the time to map perception can make thoughtful and precise moves in their markets. This kind of strategy can make the difference between a business that fails and a business that thrives.
Perceptual mapping is one of many practical tools you will learn if you work through a good business program. Whether you pursue a Business Certificate or a Marketing Degree program, the curriculum at Rasmussen focuses on real world problems and useful strategies like this.
Learn more at the Rasmussen Business Program page.




